This post is part of an ongoing series originally published around 2010, examining the misandry embedded in mental health research. It’s the first of three research projects covered in that series. This one looks at a report from Great Britain’s NSPCC on teen violence — and it’s astonishingly misandrist. It’s worth reading just to see how deftly they twist language to push their narrative. I’ve included links at the end, along with images of media articles that dutifully echoed their claims. It’s remarkable how easily the media amplifies these lies and half-truths — and has been doing so for years. The remaining two posts in the series will be published over the next two Saturdays.
— Tom

Teen Violence — When Ideology Trumps Data
The first project we’ll look at is a study from Great Britain on teen relationship violence. The research included both a written survey and in-depth interviews with selected teens. The survey results were clear: both boys and girls experienced relationship violence.
Yet, the public ad campaign that followed told a very different story. It focused entirely on helping girls as victims and portrayed boys only as perpetrators. This stunning disregard for male victims — and for the girls identified as perpetrators — stood in sharp contrast to the study’s own data. Those numbers showed that many boys were victims of teen relationship violence, and that girls, too, could be perpetrators.
Let’s start at the beginning — with how this issue first caught my attention.
A friend emailed me a link a couple of months ago to an article from Great Britain about teen violence. The friend was worried that the article was biased against boys. Here’s how it started:
A new government campaign launched today urges teenage boys not to abuse their girlfriends.
TV, radio, internet, and poster ads will target boys aged 13 to 18, aiming to show the consequences of abusive relationships.
Officials describe it as part of a broader effort to reduce domestic violence against women and younger girls.'
The campaign was inspired by research published last year by the NSPCC, which reported that:
One in four teenage girls said they had been physically abused by a boyfriend.
One in six said they had been pressured into sex.
One in three said they had gone further sexually than they wanted to.
I was a bit taken aback by the article, especially given the recent research on teen relationship violence showing that it tends to be fairly symmetrical — with both boys and girls acting as perpetrators and victims. Yet this article presented a very different picture. It assumed from the outset that girls were the primary victims and boys the primary perpetrators, reflecting an outdated stereotype about domestic violence.
That disconnect made me wonder what was really going on. I read several more articles about the ad campaign mentioned in the piece, and was surprised — even shocked — to find that the campaign’s entire focus was on helping girls while “teaching” boys not to abuse their girlfriends.
Each of these articles cited the same research as the basis for the campaign. So I decided to go straight to the source and see what the original study actually found.
The original study was sponsored by the National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children (NSPCC) of Great Britain and was in two parts. The first part was the “full report” and was a detailed 209 page research report explaining methodology, results, implications and conclusions. The next was the Executive Summary which was a 10 page summation of the findings of the full report. It was a quick read meant to give people the essence of the larger document. I read through the “full report” and then the executive summary. It was striking to me that the data in the full report actually showed that boys were victims of teen violence. The original news article I had read had mentioned that the research had found that 25% of girls said they had been physically abused by their boyfriends. What the news article omitted saying was that the same research had also found that 18% of boys had said that they had been physically abused by their girlfriends. This meant that this research found that almost half of the victims of teen relationship violence were boys! Somehow this important fact had been omitted from the news report.
There were plenty of other headlines that could have been drawn from the data of the full report that showed the boys to have been victims and the girls perpetrators but they were nowhere to be seen in any of the news articles. Here are a couple of examples of headlines that could be written from the data of the full report:
25% of those reporting physically forcing their partners into having sexual intercourse were girls – Table 15 page 82 full report
Nearly three times as many girls reported using SEVERE violence in relationships. table 11 – page 75 full report
Over three times as many girls reported using partner violence in their relationships table 10 page 74 full report
Over 1/3 of those reporting being pressured into kissing, touching or something else were boys. table 6 page 66 full report–
Nearly half (42%) of the victims of teen relationship violence were boys Table 3 page 44 full report
Nearly one third of the victims of severe violence were boys Table 4 page 45 full report
Twice as many girls reported physically forcing their partners into “kissing, touching, or something else” more than a few times. Table 13 page 82 full report
This is just a sampling of the findings from the full report. It’s clear that the survey showed teen relationship violence was not gender-based — both boys and girls were represented among the victims and perpetrators. However, after reading both the full report and the executive summary, I noticed a striking difference. The full report included data showing boys as victims and girls as perpetrators, but the executive summary contained far less information about male victims and female perpetrators. In fact, the executive summary seemed to focus almost entirely on female victims and male perpetrators.
I began to wonder how such a shift could occur. The original study had shown boys as victims — not as frequently as girls, but still in significant numbers. Boys accounted for roughly 25–42% of victims, certainly not the majority, but far too many to ignore. Yet ignore them they did.
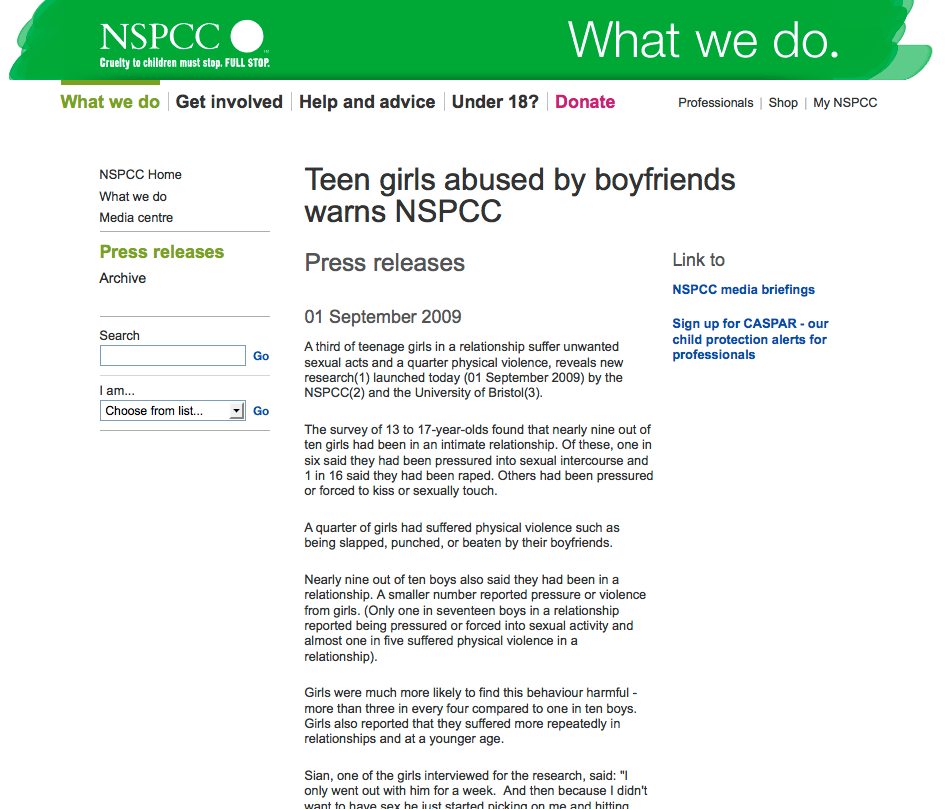
The NSPCC introduced this research to the public through a press release, and once again, we can see the same pattern — a steady move away from acknowledging boys. What began as an apparently balanced investigation into teen relationship violence in the full report became less so in the executive summary, and by the time it reached the press release, the focus had shifted almost entirely to girls. Here’s the opening of that release. Note the “girls only” framing in both the headline and the opening paragraphs:
Teen girls abused by boyfriends warns NSPCC Press releases 01 September 2009 A third of teenage girls in a relationship suffer unwanted sexual acts and a quarter physical violence, reveals new research(1) launched today (01 September 2009) by the NSPCC(2) and the University of Bristol(3). The survey of 13 to 17-year-olds found that nearly nine out of ten girls had been in an intimate relationship. Of these, one in six said they had been pressured into sexual intercourse and 1 in 16 said they had been raped. Others had been pressured or forced to kiss or sexually touch. A quarter of girls had suffered physical violence such as being slapped, punched, or beaten by their boyfriends.
Girls are highlighted repeatedly in the press release. If one only read the press release you might assume that the boys were incidental and that the girls were clearly the identified victims of teen relationship violence. The boys actually did get mentioned in one paragraph (one out of 18 paragraphs, eleven of which were about girls). Here it is:
Nearly nine out of ten boys also said they had been in a relationship. A smaller number reported pressure or violence from girls. (Only one in seventeen boys in a relationship reported being pressured or forced into sexual activity and almost one in five suffered physical violence in a relationship).
Note how the boys victimization is minimized with words like “a smaller number” and “only one in seventeen.” Keep in mind that the “smaller number” referred to in the second sentence was 18% versus 25% which had been the figure for girls. While 18 is smaller than 25, it is not that much smaller. Another important difference is that the girls 25% stat was mentioned in the opening sentence of the document (and indirectly in the headline) while the boys 18% stat was mentioned as an afterthought in parentheses. Yes, the boys percentage was smaller but it seems very obvious that this press release is trying to marginalize the victimization of boys.
Note that the press release mentions that one in 17 girls had been raped. This works out to about 5.8% of the females surveyed. What they don’t mention is that the same table in the full report that showed that 5.8% of girls were raped also showed that 3.3% of the boys were also raped. This stat never made it beyond the full report. The press release mentions the rape of girls but is completely silent on the shocking statistic that 3.3% of the boys were raped. The fact is that their data from the full report shows boys comprised over one third of the rape victims. Not a word about this.
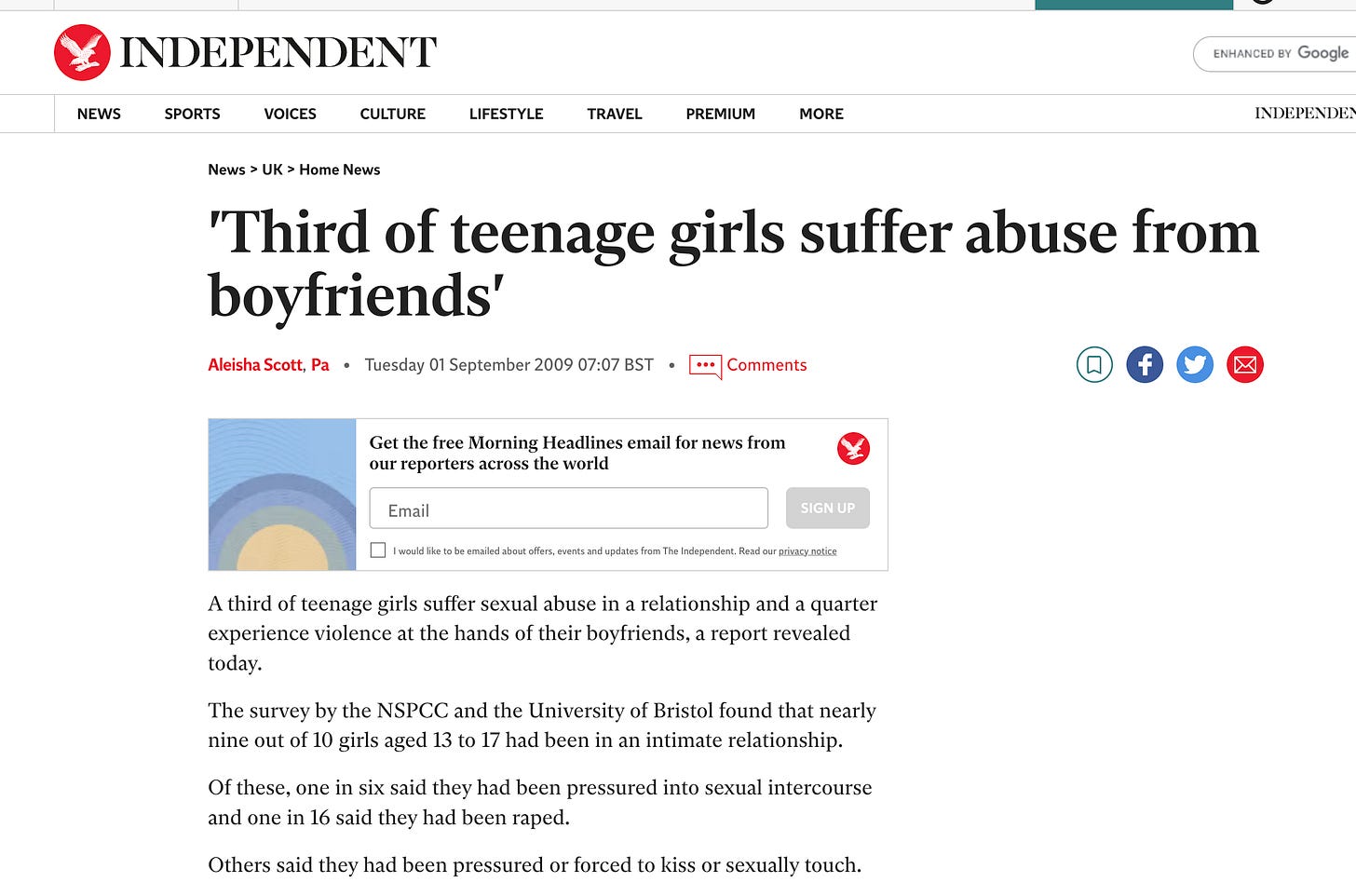
It now seems easy to understand how the media articles focused so exclusively on girls and ignored the needs of boys. They likely only read the press release and maybe a part of the executive summary. The press release might very well have been the only document they read about the study and it clearly focused almost exclusively on girls while ignoring the needs of boys. How bad did it get in focusing on just girls? Here is a sampling of typical headlines from actual news articles on this research and ad campaign: Many Girls’ Abused by Boyfriends
Third of teenage girls forced into sex,
NSPCC survey finds
1 in 3 Teenage Girls Tell of Sexual Abuse by Their Boyfriends
Teen Girls Abused by Boyfriends Warns NSPCC
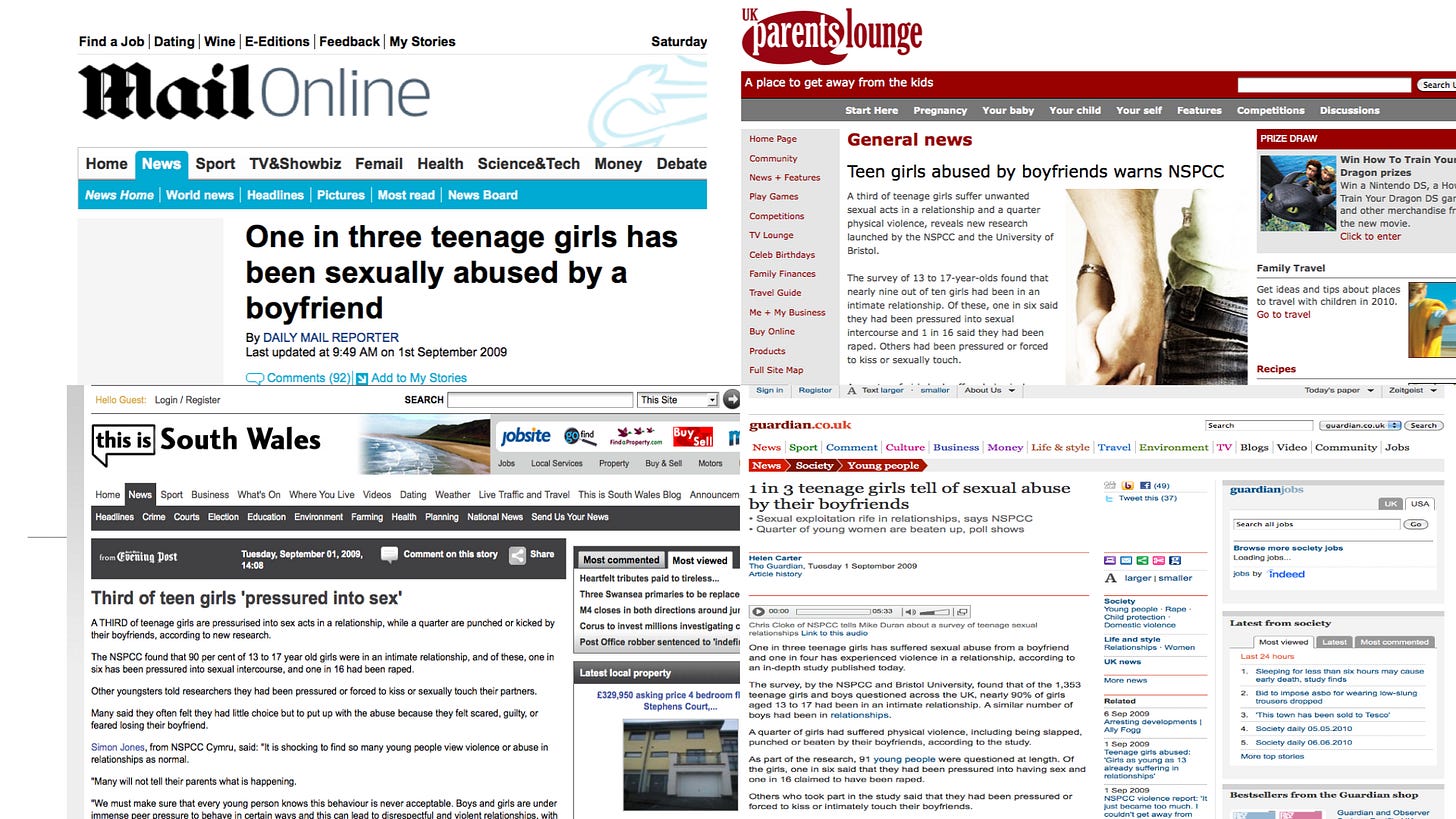
Almost every headline I found focused on girls as victims. Not one centered on boys. The articles occasionally mentioned that boys could also be vulnerable, but the main narrative was always about girls’ vulnerability and victimhood.
The ad campaign represented the real-world application of this research — TV, radio, internet, and poster ads aimed at changing teen relationship behaviors. It marked the point where theory ended and where public messaging — and taxpayer funding — began.
Inexplicably, the campaign’s focus was entirely on girls as victims of relationship violence, while boys were portrayed as the problem and instructed not to abuse their girlfriends. Somehow, the original research had shown that both boys and girls experienced relationship violence, yet by the time the findings reached the media — and then the public through the ad campaign — the data on male victims had all but disappeared.
How did this happen?

The Full Report and then boys disappear
The full report offers an abundance of data that shows that boys are victims of teen partner violence but somehow the recommendations of both the full report and the executive summary seem to focus primarily on girls. Here’s a quick summary extrapolated from the full report:
According to their survey:
*** 72% girls reported experiencing emotional violence 51% of boys reported emotional violence BOYS WERE 41% of the victims of emotional violence in teen relationships
*** 25% of girls experienced physical partner violence 18% of the boys experienced physical partner violence BOYS WERE 42% of the victims of physical partner violence in teen relationships
*** 31% of girls experienced sexual partner violence 16% of boys experienced sexual partner violence BOYS WERE 34% of the victims of sexual partner violence in teen relationships.
According to the survey, boys made up between 34% and 42% of the victims. The full report stated this clearly in the data. Yet, as the findings moved from the full report to the executive summary and then to the press release, boys seemed to vanish. Why could that be?
The researchers never directly explained this omission, but reading between the lines, two possible reasons emerge.
The first is that the survey results suggested girls were more “impacted” by relationship violence than boys. One question on the survey asked about emotional reactions to the violence. Girls were far more likely to select responses indicating they felt scared, upset, or humiliated. Boys, on the other hand, were more likely to report feeling angry, annoyed, or unaffected.
The researchers appear to have interpreted these emotional differences to mean that girls suffered more deeply from relationship violence — and therefore should be the primary focus of attention and services. This assumption is implied in several places throughout the full report. Here’s one example:
This research has demonstrated that a fundamental divide exists in relation to how girls and boys are affected by partner violence, and this divide needs to be a central component in the development of professional responses to this issue.
What exactly does “professional responses to this issue” mean? The authors never explain, but it seems reasonable to assume they’re suggesting that girls should receive more attention and services because they were more emotionally affected by the violence. Given that the report’s recommendations focus almost exclusively on girls while ignoring the needs of boys, this interpretation seems well-founded — though I’d be happy to be corrected if that assumption is wrong.
The researchers appear willing to overlook their own substantial evidence that boys were also victims of relationship violence — simply because girls reported stronger emotional reactions. Here’s another example:
These findings are further elaborated on in the interview data where girls consistently described the harmful impact that the violence had on their welfare, often long term, while boy victims routinely stated they were unaffected or, at the very worst, annoyed. These results provide the wider context in which teenage partner violence needs to be viewed.
It’s important to remember that the interview data quoted above — which we’ll examine in more detail later — included only 62 hand-selected girls and 29 similarly chosen boys. Notably, only one of those 29 boys was a victim of non-reciprocal violence. That makes it highly questionable to draw broad conclusions from such a small and uneven sample, especially when the survey itself included over 1,300 teens.
Also worth noting is the phrase “the wider context in which teenage partner violence needs to be viewed.” We can reasonably assume the researchers are again implying that girls should receive priority in services and support. What’s clear, however, is that the data on violence against boys is ignored — both in the recommendation sections and in the resulting ad campaign. The following quote offers further insight into the researchers’ perspective:
Intervention programmes need to reflect this fundamental difference by ensuring that the significant impact of violence on girls’ wellbeing is recognised and responded to, while enabling boys to recognise the implications of partner violence for their partners and themselves.
This statement clearly shows that the researchers believe that the girls should be treated differently and intervention programs need to “reflect” the difference that girls are more impacted by the violence.
But are girls more impacted? I am not so sure. Let’s start by looking at the actual question on the survey:
3 How did it make you feel when force was used against you? scared/frightened angry/annoyed humiliated upset/unhappy loved/protected thought it was funny no effect
The researchers noted that boys and girls gave markedly different responses when asked how the violence had affected them. However, they didn’t provide the raw data — no breakdown of how many boys or girls chose each option — only a summary stating that girls were much more “impacted.”
There are good reasons for this difference. The question itself was flawed — practically designed to produce a gender gap. Boys and girls are socialized, and often biologically inclined, to respond to emotional threat differently. The creators of this survey question seemed unaware of boys’ deep-seated reluctance to show vulnerability or dependence — a reflection of their hierarchical nature and their drive for independence.
For a boy to check boxes like “scared/frightened,” “humiliated,” or “upset/unhappy” would mean admitting weakness, something most boys instinctively avoid. Instead, they are far more likely to select “angry/annoyed” or even “no effect” to maintain an image of strength. As Warren Farrell aptly said, “The weakness of men is the facade of strength; the strength of women is the facade of weakness.” Boys and men are far more likely to choose responses that convey control and toughness.
If this is true, then boys’ responses in the survey may not accurately reflect their true emotional impact. It’s entirely possible that those who checked “no effect” were just as hurt or disturbed as their female counterparts. With questions framed this way, we’re left not knowing the real story. Basing future services on such data would be risky — and likely lead to deeply flawed conclusions.
Consider this: would the researchers dismiss a rape victim who said she felt “no impact” and decide she didn’t need support? Of course not. Would clinicians ignore domestic violence victims who claimed they were unaffected? Hardly. So why dismiss the pain of boys simply because they reported fewer signs of distress on a survey? Emotional reactions vary widely from person to person, and not showing immediate or visible distress doesn’t mean the trauma isn’t real.
Having worked with trauma victims for many years, I know that emotional impact often emerges slowly — sometimes months or even years after the event. To deny services based on someone’s initial emotional response, or apparent lack thereof, is one of the most misguided ideas imaginable. And to deny those services to an entire group — in this case, boys — on that basis isn’t just poor reasoning. It’s prejudice, plain and simple.
Are the researchers biased against boys?
There are numerous indications, in addition to what has already been described, that the researchers have an anti-boy bias. There are the obvious dismissals of the survey data that shows boys to be victims of partner violence and the complete focus on girls as victims. But there are a number of more subtle clues in the study that seem to indicate a disdain for boys.
When they did mention boys as victims the report tended to minimize their experience. Here is a quote:
Boys’ experiences of violence - Little evidence existed to support the possibility that boys, although they were negatively affected by their partner’s violence, felt unable either to voice or to recognise their vulnerability. Boys minimised their own use of violence as “messing around”. Boys also reported the violence as mutual, although they often used disproportionate force compared to their female partners.
Rather than addressing boys’ actual experiences of violence, the researchers focused on whether the boys could “give voice” to the negative effects of their partners’ aggression. This seems like a weak attempt to suggest that boys were able to articulate their experiences — and therefore must not have been “held back” by traditional masculinity from expressing vulnerability. The unspoken implication is that because boys could talk about their victimization, they must not have been deeply affected by it. In other words, it didn’t really matter for them — whereas for girls, it did.
This framing distracts from the central reality: the boys were victims of violence. Reading the researchers’ words makes it clear how differently boys were treated in this study. Their pain was minimized and rationalized away, reduced to the notion that they simply weren’t as impacted. The underlying message was that yes, boys experience violence from their female partners, but they don’t suffer from it in the same way.
That conclusion runs counter to everything we know about male psychology. It’s well established that men and boys often minimize their pain, hide their injuries, and strive to maintain an appearance of independence. This doesn’t mean they’re unaffected — it means they’re reluctant to show it. Precisely because of this tendency, we need a different approach when addressing victimization among boys.
Unfortunately, this study chose another route: it largely ignored boys’ pain and focused its empathy and attention almost exclusively on girls.
Messing Around
The quote above states that “boys minimised their own use of violence as ‘messing around.’” According to the full report, boys described their behavior this way 56% of the time. This finding is later cited in the recommendations section as justification for teaching boys to recognize and take responsibility for their violence. (See below.)
But what about the girls? You might assume that since boys were singled out for this attitude, girls must have responded differently. Not so — at least not in the curious, upside-down logic of this study. By the researchers’ own data, girls described their own violence as “messing around” 43% of the time — only 13 percentage points less than the boys.
Given that both sexes minimized their aggression in similar ways, it would make sense that both boys and girls should be encouraged to recognize and take responsibility for their actions. Yet the recommendations focus solely on boys. That’s not sound reasoning — it’s bias. Specifically, an anti-boy bias.
Here is the quote:
“However, although intervention programmes should ensure that the needs of both girls and boys are recognised, it is important that the wider experiences of girls remain a focus. In addition, boys’ minimisation of their own use of violence – by dismissing it as “messing around” and justifications based on mutual aggression – needs to be challenged.”
Why would the boys need to be challenged about this and the girls not? The boys said their violence was “messing around” 56% of the time and the girls said their violence was a slightly lower “messing around” 43% of the time. Clearly a strong bias in favor of girls and against the boys.
The researchers went a step farther than just recommending that girls victimization should be the focus. The researchers made the claim that boys lower scores on the impact question actually made them more dangerous to their female partners. Here is a quote:
If boys view the impact of their victimisation as negligible, they may also apply this understanding to their own actions. Thus, they may believe that their partners are also unaffected by their use of violence.
The implication here is that boys’ supposed insensitivity to the violence done to them makes them less sensitive to the violence they might commit. I find that hard to believe — especially considering that nearly every boy grows up hearing, over and over, that he must never hit a girl.
Let’s apply the same reasoning to girls. According to the survey, girls reported being far more emotionally affected by relationship violence than boys. Yet those same girls also admitted to using violence three times more often than boys did. If we follow the researchers’ logic, this would suggest that girls are well aware of how hurtful violence can be — and still choose to use it far more frequently. That hardly paints them in a positive light, does it?
The researchers conclude:
Thus, from these findings it seems conclusive that partner sexual violence represents a problem for girls, while boys report being unaffected.
That sums it up rather neatly — and disturbingly.
Boys are More Violent? When the Subjective Trumps the Objective
While the survey was supposed to be the main source of data, the researchers seemed to place far more weight on the subjective material gathered through interviews. The full report’s survey data clearly showed that girls were three times more likely to report using violence in relationships. Yet, somehow, the researchers claim there was “a clear consensus” among the girls that boys were more physically violent toward their partners than girls were.
Here’s the quote:
“There was a clear consensus within girls’ accounts that boys used physical violence in relationships more often than girls. This common understanding regarding the gendered nature of physical violence was reported by almost all girls, whether they themselves had experienced violence or not.”
This excerpt from page 94 of the full report summarizes the researchers’ evaluation of the girls’ interviews. The most striking aspect is the sharp contradiction between the survey data and the interview findings. The survey clearly showed that girls were three to six times more likely than boys to report being violent in relationships. Yet the subjective data from the interviews claimed that there was a “common understanding regarding the gendered nature of physical violence” — that “almost all girls” believed “boys used physical violence in relationships more often than girls.”
That’s a major discrepancy. One half of the study shows girls admitting to much higher rates of violence, while the other half asserts that boys are the primary aggressors. Such a contradiction demands an explanation, but the report offers little. The closest the researchers come is to suggest that girls’ higher rates of reported violence were due to acts of self-defense — an all-too-familiar claim.
However, the numbers tell a different story. According to the data, 25% of girls and 8% of boys reported being violent in relationships. When we subtract the portion attributed to self-defense — 44% for girls and 30% for boys — we find that 14% of girls and 5.6% of boys used violence for reasons other than self-defense. That means girls were nearly three times more likely than boys to commit non–self-defense violence.
This difference is substantial and should have been a central point in the report. Instead, it was ignored. The researchers’ conclusion — that girls viewed boys as more violent and therefore girls need services while boys need behavior correction — is baffling. It defies their own data and reveals a clear bias. In short, this isn’t just poor analysis. It’s misandry disguised as research.
One partial explanation of this is shown in the following quote:
Only 6 per cent of boys, compared to a third of girls, claimed that they were negatively affected by the emotional violence they experienced. This gendered impact disparity upholds Stark’s (2007) contention that coercive control, which many of our components of emotional violence reflect, is made meaningful only when placed within a gendered power understanding of intimate violence. Thus, although girls had used emotional violence, without it being underpinned by other forms of inequality and power, their attempts were rendered largely ineffectual.
Incredibly, this section seems to be giving girls a pass for their emotional violence. The pattern continues: When girls are perpetrators they are given excuses, when boys are victims they are ignored and minimized.
Reporting oddities
When you look closely at the section about girls reporting more frequent perpetration of violence in relationship you notice something very odd. Look at the following paragraph and note the researchers choice of words. Note that girls “report” and boys “admit” (emphasis mine):
Page 74 More girls reported using physical violence against their partner than did boys; this represented a significant difference (x2 (1) = 60.804, p<.001). A quarter (n=148) of girls compared to 8 per cent (n=44) of boys stated that they had used some form of physical violence against their partner. Looking first at less severe physical violence (see table 10), the vast majority of girls (89 per cent) reporting the use of physical violence had used it once or a few times. Only a few (11 per cent) used it more frequently. Similarly, the small proportion of boys who admitted using physical violence also generally used it infrequently (83 per cent).
Perhaps the words “report” and “admit” have different meanings in Great Britain but here in the US they aren’t usually the same. Report generally means to make a statement or announcement. The word admit however has a different spin. Often it has more to do with conceding or confessing. One assumption from the wording the researchers have chosen would be to think that they simply didn’t believe what the boys reported. In other words they would only concede or admit to a certain amount of violence. Basically, implying that they are not telling the entire story. This is of course conjecture on my part but it simply seems like more anti-boy bias.
The Interview Section
As was previously explained the research had both a quantitative section and qualitative section. The qualitative section consisted of semi-structured interviews which included the utilization of five vignettes. The vignettes were stories that were told to the participant and then the stories relevance was discussed as a part of the interview. The stated goals of the researchers was to use the quantitative survey to gain data and use the interviews to enhance their understanding.
The researchers claimed that they had problems in getting participants for the interviews in the manner they had originally planned so they switched mid-stream to a different approach described below:
“We therefore moved to a system whereby researchers observed which young people seemed to be engaging with the survey. They then asked those young people if they would like to take part in the interview stage.”
So they hand picked the interview participants based on their own subjective impression of whether the young person was “engaging with the survey.” This sounds to me to be a direct invitation to a very biased sample. Then you find out that the choices they made of those who were “engaging in the survey” were 62 girls but only 29 boys. You also find that of the 29 boys only one had experienced being a victim of non reciprocal violence in relationship! Makes you wonder about their ideas of “engaging in the survey.” Needless to say the boys section describing the interviews was only 22 pages long while the section about the girls was over 60 pages. Even with such a short section for the boys, most of the writing was about boys violence not their reaction to being victims of violence. Girls victimization was highlighted as was boys violence. Even in the section on boys as victims.
The Vignettes
When I first began examining this survey, I emailed the NSPCC to request copies of the original questionnaire and the vignettes used in the study. To their credit, they kindly sent both. I had suspected that the vignettes would be biased toward portraying girls as victims — and I wasn’t disappointed.
Of the five vignettes, most centered on boys’ possessiveness, shouting, name-calling, violence, or sexual pressuring. Only one story depicted a girl as the perpetrator, and even then, her behavior was relatively mild: she and her friends stole a boy’s cell phone, made unkind comments, and the next day apologized. In contrast, the other four stories featured boys engaging in clearly abusive or coercive behavior, including physical aggression and unwanted sexual advances. In one case, a girl used violence — but only in self-defense.
To the researchers’ credit, the first three vignettes included a follow-up question asking whether similar behavior might also occur with the opposite sex. But inexplicably, that question was omitted from the final two vignettes — the ones dealing with sexual pressure. This omission is telling. It suggests a possible ideological bias that prevented the researchers from viewing boys as potential sexual victims or girls as possible perpetrators. This is especially puzzling since the full report’s own data showed that many girls freely admitted to sexually pressuring their boyfriends. So why exclude the question in the interview phase?
Imagine if the situation were reversed — if 80% of the perpetrators in the vignettes had been female, and the only male perpetrator had merely stolen a cell phone and apologized. There would no doubt be loud outcries about bias, marginalization, and the lack of inclusivity — and rightly so. Yet this imbalance seems to have gone unnoticed. These vignettes marginalized the boys in the study, likely leaving them feeling misunderstood and excluded, since their experiences were neither portrayed nor acknowledged.
It wouldn’t have been difficult to design a more balanced approach. The researchers could have kept the same five stories but reversed the genders for half the participants — telling the same scenarios from both male and female perspectives. That small change alone would have ensured that both boys and girls saw their realities reflected. Alternatively, they could have used gender-neutral names for all participants, leaving the sex of the offender and victim unspecified, or created six vignettes — three with male perpetrators and three with female perpetrators — each covering different types of violence.
Any of these approaches would have been far superior to what was used.
The fact that four out of five vignettes portrayed girls primarily as victims and boys as perpetrators — and that any mention of girls as sexual aggressors was entirely absent — is further evidence of ideological bias. This project clearly reflects a worldview that insists on seeing women and girls as victims and men and boys as oppressors. Allowing such bias to persist does a disservice to everyone. It fails our boys by denying their experiences — and fails our girls by teaching them a distorted view of reality. If this kind of bias is allowed to continue in the social sciences, the credibility of the field itself is at risk.

Recommendation Section
Here’s a brief look at the recommendations section of the executive summary. There is only one paragraph in the recommendation section that mentions boys. Here it is:
Impact of teenage partner violence – the gender divide The impact of partner violence is indisputably differentiated by gender; girl victims report much higher levels of negative impact than do boys. This is not to imply that boys’ experiences of victimisation should be ignored. It may be that boys minimise the impact of the violence due to the need to portray a certain form of masculinity. However, although intervention programmes should ensure that the needs of both girls and boys are recognised, it is important that the wider experiences of girls remain a focus. In addition, boys’ minimisation of their own use of violence – by dismissing it as “messing around” and justifications based on mutual aggression – needs to be challenged.
This paragraph is baffling. Let’s break it down. Here is the first section:
The impact of partner violence is indisputably differentiated by gender; girl victims report much higher levels of negative impact than do boys. This is not to imply that boys’ experiences of victimization should be ignored.
It first makes a claim that partner violence is differentiated by gender and that girls experience more negative impact, implying that boys should be ignored. Then they deny that they mean to ignore boys.
It may be that boys minimise the impact of the violence due to the need to portray a certain form of masculinity.
They offer a possibility for an explanation.
However, although intervention programmes should ensure that the needs of both girls and boys are recognised, it is important that the wider experiences of girls remain a focus
Then they ignore their own explanation and aver that the “wider experiences of girls” (whatever that means) should take precedence.
In addition, boys’ minimization of their own use of violence – by dismissing it as “messing around” and justifications based on mutual aggression – needs to be challenged.
The researchers conclude by emphasizing that the focus should be on boys — specifically, their use of violence and their tendency to minimize it, as discussed earlier.
I find this paragraph deliberately vague. My guess is that the ambiguity is intentional. They can’t quite say what they mean — that girls are seen as worthy victims and boys are not — because putting that bias into words would make it too obvious. Vagueness, then, becomes a safer strategy: it conceals the prejudice while still advancing it. What’s clear after reading is that, for whatever reason, girls are portrayed as deserving the lion’s share of help and services, while boys are told to “shape up.”
Is Ideology Driving the Research?
Viewed purely from a marketing standpoint, these researchers achieved something remarkable. They managed to produce a document labeled as a “study,” gather objective data, then draw conclusions that contradicted their own findings — and still have those conclusions echoed across major media outlets. The result: millions of people were presented with half-truths packaged as scientific fact. That’s quite an accomplishment, if one’s goal is persuasion rather than truth.
It’s hard to escape the impression that the researchers are clinging to a dated feminist narrative — one that insists domestic violence is a story of male perpetrators and female victims. Yet as Murray Straus and many others have shown, that model has long been disproven. The persistence of this bias shows how far some are willing to go to preserve a comforting ideology rather than face complex realities.
Science, at its best, collects data and adjusts theory based on what is discovered. But in this case, ideology appears to be steering the science. The researchers seem to have decided in advance that girls were the victims and boys the aggressors. When their data failed to confirm that assumption, they reinterpreted it to fit the narrative. Their central claim — that girls should be the focus of attention because they are “more impacted” — is a hollow one. Emotional distress does not determine moral worth or entitlement to support. No ethical researcher would argue that some victims deserve less services simply because they express less visible pain.
Many parts of this study struck me as blatantly misandrist — so much so that I could easily write another twenty or thirty pages dissecting them. I’ll spare the reader that, but suffice it to say this study stands as a cautionary example of what happens when ideology guides research, shapes public policy, and filters what the public is told.
This is precisely the danger of allowing ideological zealots to shape public opinion under the banner of “science.” We need to be far more discerning about what qualifies as legitimate research, and far quicker to expose studies compromised by bias. Any high school science student could point out the flaws in this one — yet our media and governments either can’t, or won’t. That failure has consequences for everyone who depends on honest science, balanced reporting, and fair treatment of all victims.
Men Are Good.

____________________________
Link to the full study https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265245739_Partner_Exploitation_and_Violence_in_Teenage_Intimate_Relationships
Some old news stories that show how they hyped the narrative:
https://www.bristol.ac.uk/news/2009/6524.html
http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8230844.stm
https://www.theguardian.com/society/2009/sep/01/teenage-sexual-abuse-nspcc-report
https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-1210375/One-teenage-girls-physically-abused-boyfriend.html
Here’s a partial screen shot of the press release. The links for both the executive summary and the press release are now gone.